Plate heat exchanger in Gas-plants and Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) Applications
Heat exchangers are used in natural gas processing plants for gas drying, preheating natural gas, gas sweetening or the liquefaction of natural gas. Plants for the industrial production of gases such as ammonia, synthesis gases or hydrogen also include thermodynamic processes. GESMEX plate heat exchangers operate in gas plants as liquid coolers, gas coolers, condensers, evaporators, partial condensers or partial evaporators.
Natural gas drying by LTS process (low-temperature separation)
The natural gas (NG) of a bore is saturated with water vapor and must be dried to meet the pipeline specification and maximum the calorific content, before being fed into a pipeline. Various methods can be used, however the LTS process controls the dew point of natural gas by condensating the water vapor. The experience the natural gas industry had with shell and tube condensers, showed that the mixture of the condensed water and heavy hydrocarbons at low temperatures (-5 to -15 ° C) forms hydrates. This leads to a blockage of the condensate outlet of the heat exchanger. To prevent this glycol or methanol is commonly injected into the heat exchanger gas inlet. GESMEX has developed a special heat exchanger (XPS LTS) for the LTS process, which is equipped with both a glycol injection and separate liquid outlets.
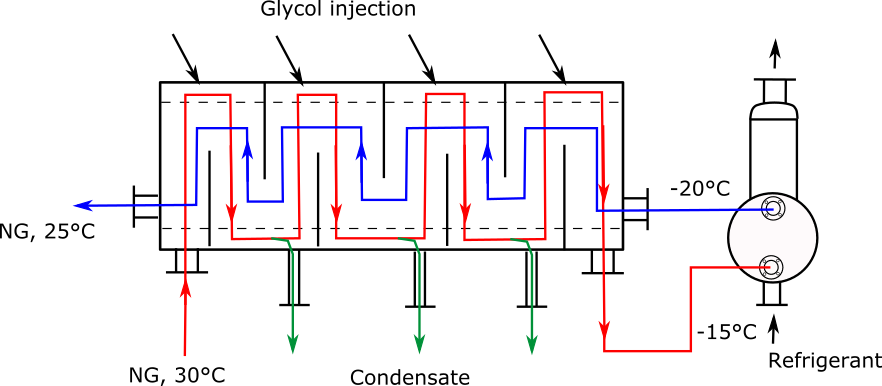
The cooling medium is the natural gas itself, through a recupertive process. The natural gas leaving the XPS LTS is cooled down in a chiller by 5 - , 10 °C and then passed back through the XPS LTS heat exchanger.
This is then reheated by the incomming natural gas and leaves the XPS LTS only a few degrees colder than it entered. This internal heat recovery leads to a dehumidification of the natural gas without the noticeably lowering the temperature, and forming hydrates. At the same time, the condensate can then be safely drained.
The chiller in the LTS process is also a GESMEX heat exchanger, an evaporator which is part of the refrigeration system. For droplet separation it was equipped with a integrated knockout pot.

- Type:
- Plate & Shell, XPS 100
- Variant:
- countercurrend flow, fully welded
- Features:
- recuperator, glycol injection, multiple drains
- Installation site:
- Germany

- Type:
- Plate & Shell, XPS 100
- Variant:
- countercurrent flow, fully welded
- Features:
- evaporating refrigerant cools natural gas
- Installation site:
- Germany
Natural gas pre-heater (Dew Point Heating)
If natural gas is expanded in a turbine, it is cooled by a phenomenon known as the Joule-Thomson-Effekt. This changes the dew point, and causes heavier hydrocarbons to condense out, which can damage downstream equipment. It also changes the calorific value of the gas, and is necessary to heat the gas.
Heat exchangers are used to heat the gas with large distributors, due to the two phase flow:
- Type:
- Plate & Shell, XPS 200
- Variant:
- openable shell on both ends
- Features:
- high-pressure, gas distribution necessary
- Installation site:
- Germany
Liquified Natural Gas (LNG)
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is increasingly playing a larger role in the global energy mix, especially in areas, where there are little or no natural gas reserves, or no pipeline network. The LNG is usually transported on ships. Large, cryogenic, heat exchangers capable of pressures up to 80 bar, are required in the liquefaction and regasification plants in inport and export terminals. For liquefying the gas must be repeatedly compressed and cooled. An effective heat transfer as in Plate and Shell heat exchangers is a great cost saving, where close temperature approaches enable a reduction in the energy required in the refrigeration plant also.

- Type:
- Plate & Shell, XPS 200
- Variant:
- fully welded
- Features:
- low temperature application Marine
- Installation site:
- Germany
Natural gas sweetening
The removal of H2S and CO2 from sour gas is called gas sweetening. The sulfur content allowed in pipeline specification natural gas is subject to a limit. If too much hydrogen sulfide is in the natural gas, it has to be removed before being fed to the pipeline. The sulfur is often absorbed with a regenerable solvent, typically amines such as MEDA, or DEA are used. Before the absorption process, the solvent must be heated, via an interchanger, and regenerated in a scrubbing tower, with a reboiler, before being cooled and put back into the absorption column. For these process steps the Plate and Shell is an ideal heat exchanger.

- Type:
- Plate & Shell, XPS 50
- Variant:
- fully welded
- Features:
- acid resistant material
- Installation site:
- Germany
Hydrogen production
In industrial production of hydrogen, light hydrocarbons from natural gas are processed to pure hydrogen. The most common method is using a steam reforming, where steam is added to a hydrocarbon mixture and is heated to react to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxid.
XPS - Plate & Shell heat exchangers are used in the steam system for condensate cooling and boiler feed water heater. Due to high temperatures, the system require high design pressures. Here the high pressure resistance of laser-welded GESMEX - apparatuses is particularly advantageous.

- Type:
- Plate & Shell, XPS 50
- Variant:
- openable shell
- Features:
- design pressure 135 bar, openable, multi-pass at plate side
- Installation site:
- Finland
Heat exchangers in utility systems and for heat recovery

In addition to process-specific tasks, GESMEX plate heat exchangers are also used in numerous auxiliary and utility systems, such as: heating of cleaning solutions, cooling lubricant oil, drying copmressed air, jacket cooling, ...
GESMEX plate heat exchangers are used for heat recovery from exhausst vapors or flash steam, in sewage systems, for heat recovery or power generation from waste gases ...
